Differential Electrochemical Mass Spectrometry (DEMS) is an analytical method that is a combination of mass spectrometry and electrochemical half-cell experimentation. It is used in continuous faradaic reactions to identify products or intermediates and for characterizing the sub-monolayer levels of adsorbates on electrode surfaces through adsorption. 1.
DEMS allows for in-situ mass resolved determination of reaction intermediates, gaseous or volatile electrochemical reactants, and products in real-time. A typical DEMS system comprises an electrochemical half-cell, membrane interface, and a vacuum system that includes a quadrupole mass spectrometer.
Why is Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Conversion so Important?
The reduction of CO2 is critically important in combatting climate change with a huge emphasis being placed on cutting emissions over the last decade. Whilst efforts are made to reduce CO2 emissions at the source and increase renewable energy efforts, it is critical to understand that burning fossil fuels is a significant aspect of society’s infrastructure.
This is why waste management is critical and why converting waste CO2 into a useful product is important. The process of converting CO2 waste requires a huge amount of energy but using DEMS can help to lower the electric potential level at which these chemical reactions take place.
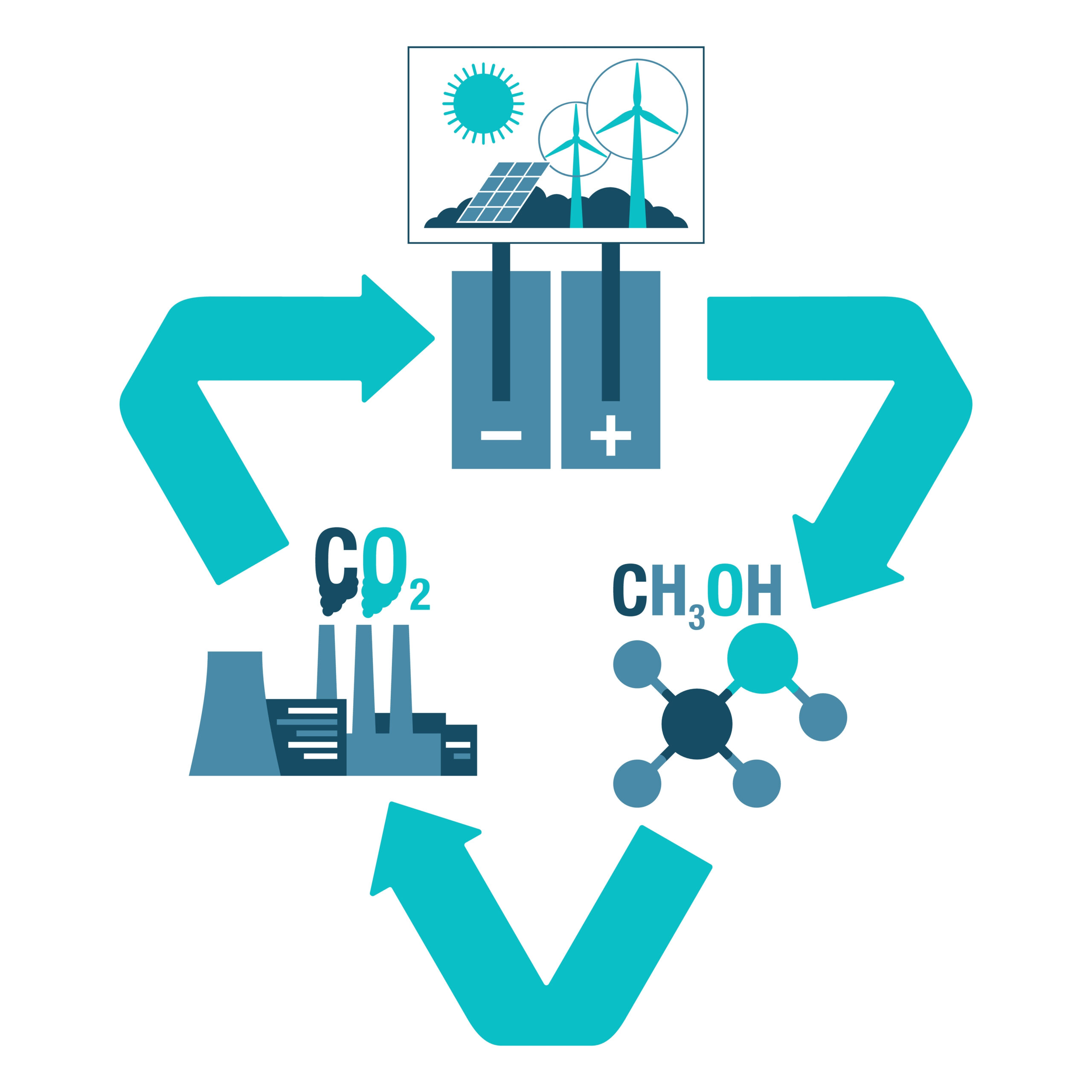
What is Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction?
Electrocatalytic CO2 reduction is a chemical process that takes electricity and converts it into a useful chemical in a direct manner. The chemical it produces could be multi carbon alcohol such as ethanol that can be used as fuel or raw material that could be used directly in the chemical industry.
Using this technology would have huge impact on CO2 emissions at places such as power plants and factories.
Why DEMS is So Beneficial for CO2 Conversion
Differential electrochemical mass spectrometry can be used for rapidly screening catalysts. Electrode voltages are rapidly scanned and reaction products are recorded in real-time via a process of interfacing the electrochemical reactor and mass spectrometer. This means that the process takes just a few hours rather than the average time of a week.
DEMS can also help to accelerate material discovery, meaning its implementation in the real world can happen a lot quicker. This technology can help significantly reduce CO2 emissions across the chemical industry and the entire world’s energy infrastructure.
Find Out More
If you would like to learn more about the benefits of using differential electrochemical mass spectrometry for CO2 conversion, you can find out more on our website.
References

