Catalytic hydrolysis of cellulose over solid acid catalysts is one of efficient pathways for the conversion of biomass into fuels and chemicals. In this study, we synthesized a novel silica catalyst by an evaporation-induced self-assembly method (EISA) and tested its activity for the catalytic selective hydrolysis of cellulose to glucose. This silica catalyst exhibited a higher catalytic activity than other oxides, such as ZrO2, TiO2, and Al2O3 etc., prepared with the same method. The 73.3% cellulose conversion with 50.1% glucose yield was achieved over this novel silica catalyst under hydrothermal conditions without hydrogen gas (Table 1).
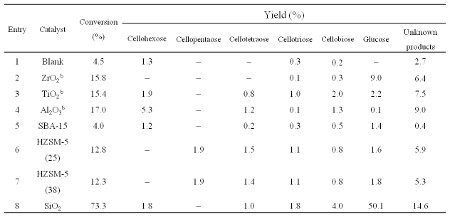
Table 1. Cellulose conversion and yield of products over different catalysts at 433 K for 12 ha
a. Reaction conditions: 12 hr reaction time, 10 mL H2O, 0.05 g cellulose, 0.15 g catalyst.
b. The preparation of catalysts were carried out under the identical experimental conditions to that of entry 8.
Temperature-programmed desorption of ammonia (NH3-TPD) using a mass spectrometer (HPR-20, Hiden Analytical, Warrington, UK) was used to characterize the acidic properties of the tested samples. The amount of acid sites was estimated by the conventional acid-base titration method. The results of NH3-TPD (Fig.1) indicated that the acidic properties of the SiO2 sample were much stronger than those of the other samples. In addition, the SiO2 sample presented a much higher acid amount than other samples. The textural properties (BET) indicated that the SiO2 sample has an appropriate average pore diameter (3.512 nm) that could facilitate the transportation of oligosaccharides and thus enhances the chances of oligosaccharides interacting with acid sites. It is concluded that the synergistic effect between the strong acidity and a suitable pore diameter of silica catalyst is one of the reasons for its high activity. In addition, the catalyst was recyclable and showed the excellent stability during the recycle catalytic runs.
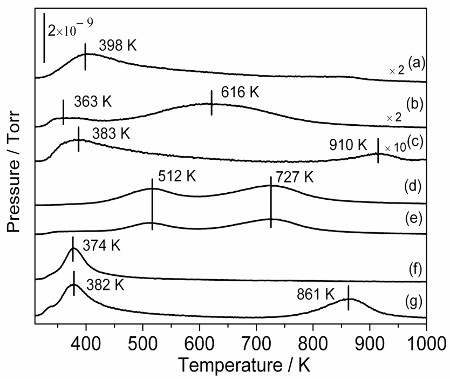
Fig. 1 Temperature-programmed desorption of ammonia (NH3-TPD) profiles for various samples of (a) ZrO2, (b) TiO2, (c) Al2O3, (d) HZSM-5(25), (e) HZSM-5(38), (f) SBA-15, and (g) SiO2 (EISA)
Project Summary By: WANG Huayu, ZHANG Changbin, HE Hong, WANG Lian, State Key Laboratory of Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology, Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100085 China

Paper Reference: Wang H., Zhang C., He H., Wang L. (2012) “Glucose production from hydrolysis of cellulose over a novel silica catalyst under hydrothermal conditions” Journal of Environmental Sciences 24 (3), 473-478
Hiden Product: HPR-20 QIC R&D Real time Gas Analyser
Read Full Article: Customer Research Review : Gas reaction studies & catalysis research [issue : 1120/10]

