Contamination with Silicone
Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) is inert, non-toxic and nonflammable and used extensively as a lubricant, in cosmetics, as a food additive [E900] and in sealants.
However, it can break down to silicon dioxide (glass) and form an insulating layer in electronics as well as forming a barrier to adhesion when bonding surfaces – it is also difficult to remove. SIMS can easily detect monolayer quantities of this important industrial contaminant.
Related Products
The positive secondary ion spectra below are from an aluminium foil before and after contact with a protective glove. A residue of PDMS from the glove manufacture has transferred to the foil and is clearly visible from the characteristic silicone peaks at m/z = 59, 73 and 147. The aluminium signal itself at m/z = 27 is also significantly attenuated by the coverage of contaminant.
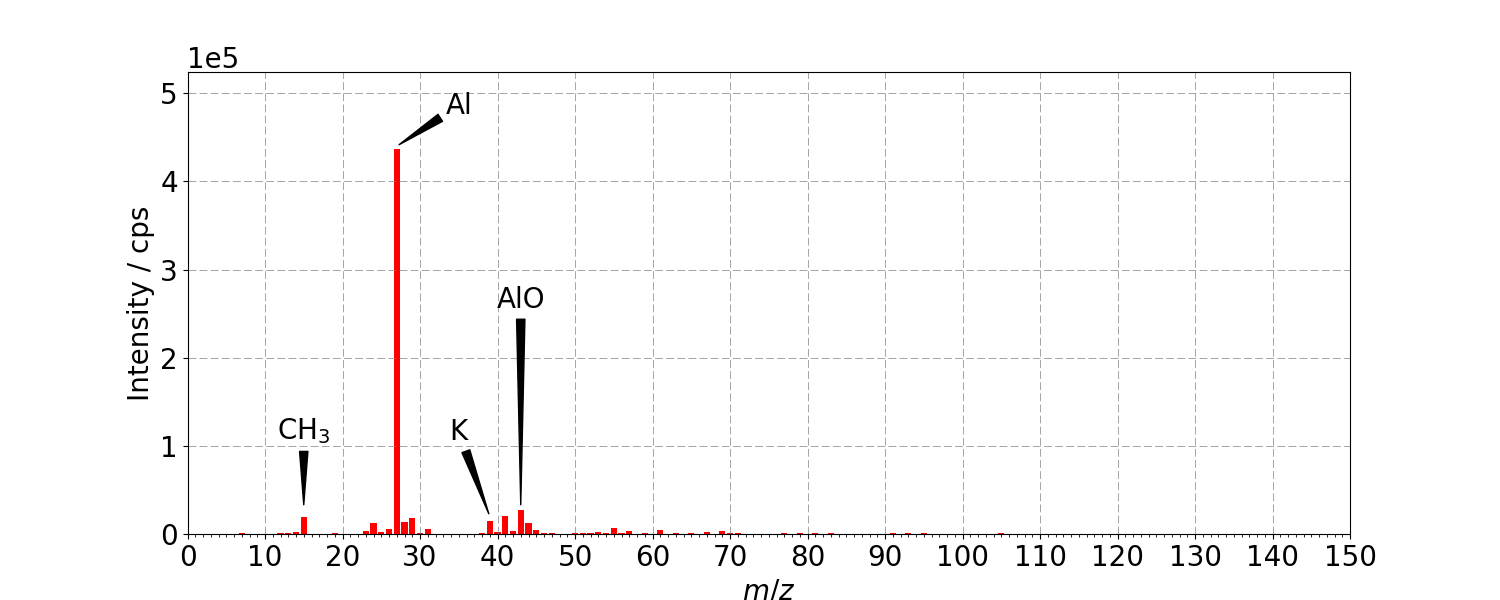
Positive ion Static SIMS of clean aluminium foil before touching with
contaminated glove
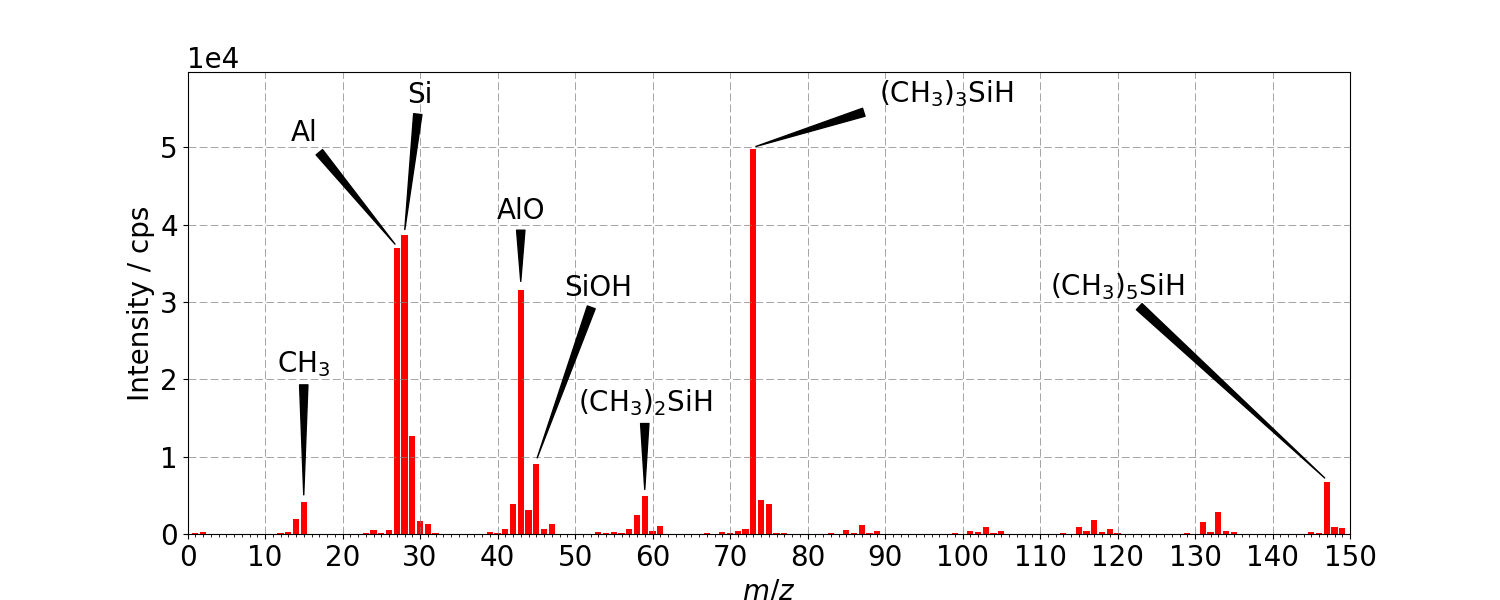
Positive Static SIMS of aluminium foil after contact with contaminated glove
Dynamic SIMS
Depth Profiling
When the ion dose exceeds the static SIMS limit (>1012 ions cm-2) there is sufficient sputtering to uncover deeper layers of the material. This allows the composition to be determined as a function of depth. SIMS depth profiles are most often used to verify layer deposition and investigate diffusion or the effects of surface chemistry, such as corrosion. The extreme sensitivity and excellent depth resolution of SIMS made the analysis of dopant profiles in semiconductors a natural early application of the technique. These pure materials formed the groundwork for robust quantification and today SIMS finds application across a broad range of industries.
Depth Resolution
In the static SIMS case the depth resolution is the uppermost atomic monolayers. In dynamic SIMS, the depth resolution is improved by reducing the impact energy, and therefore the penetration and mixing caused by the bombarding ions such that nanometre features can be resolved.
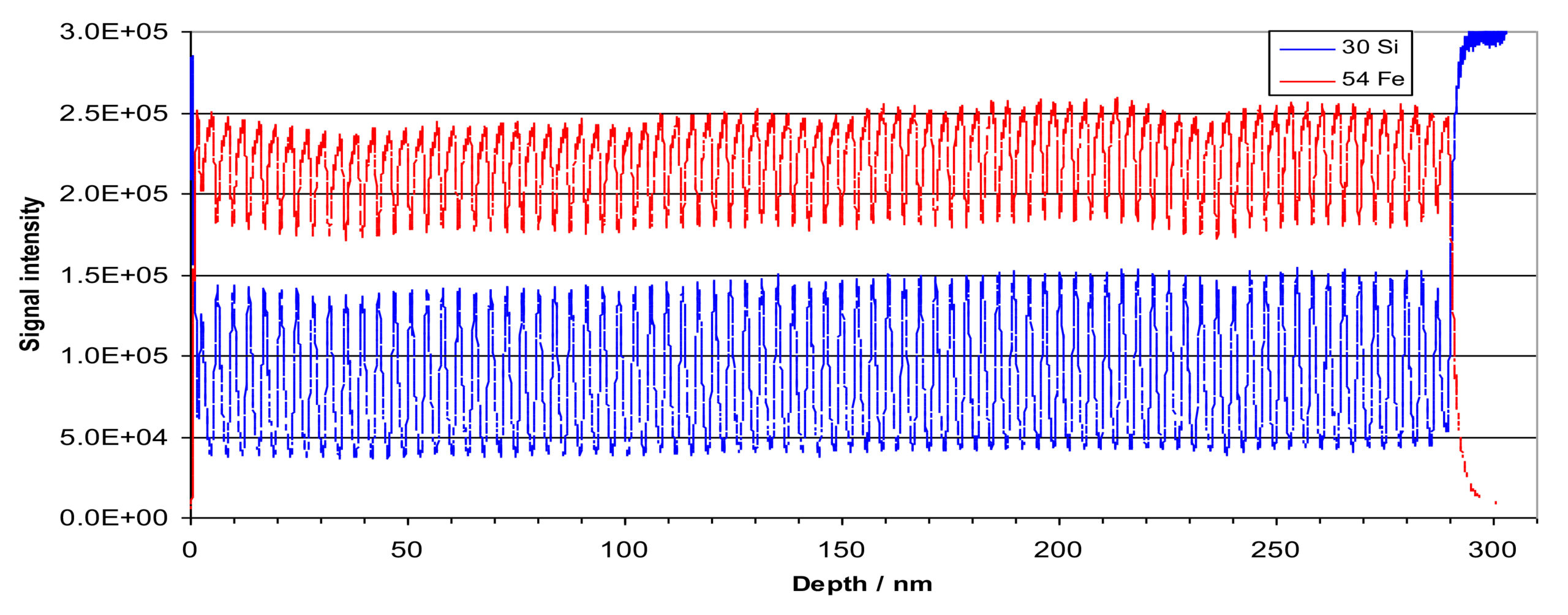 Positive ion SIMS depth profi le of a Si/Fe neutron mirror comprising 80 pairs of silicon and iron layers, each layer 1.8nm thick. Analysed using 1.5keV O2+ primary ions with oxygen flooding.
Positive ion SIMS depth profi le of a Si/Fe neutron mirror comprising 80 pairs of silicon and iron layers, each layer 1.8nm thick. Analysed using 1.5keV O2+ primary ions with oxygen flooding.
FIB – SIMS | Focussed Ion Beam Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry
Hiden Compact SIMS Mass Spectrometry in solid material
Hiden SIMS | Analytical Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry Products
Low Energy Ne Scattering from Metal Surfaces using MARISS
High Five: UHV SIMS with Plasma Primary & Simultaneous Positive and Negative Secondary Ion Detection
Contaminant Analysis with Hiden Surface Analyzers
What is Surface Interface Analysis?
Mass Spectrometers for Silicon Semiconductor Analysis
Surface Analysis Products from Hiden Analytical
How to Analyse the Top Nano Layers of a Material

